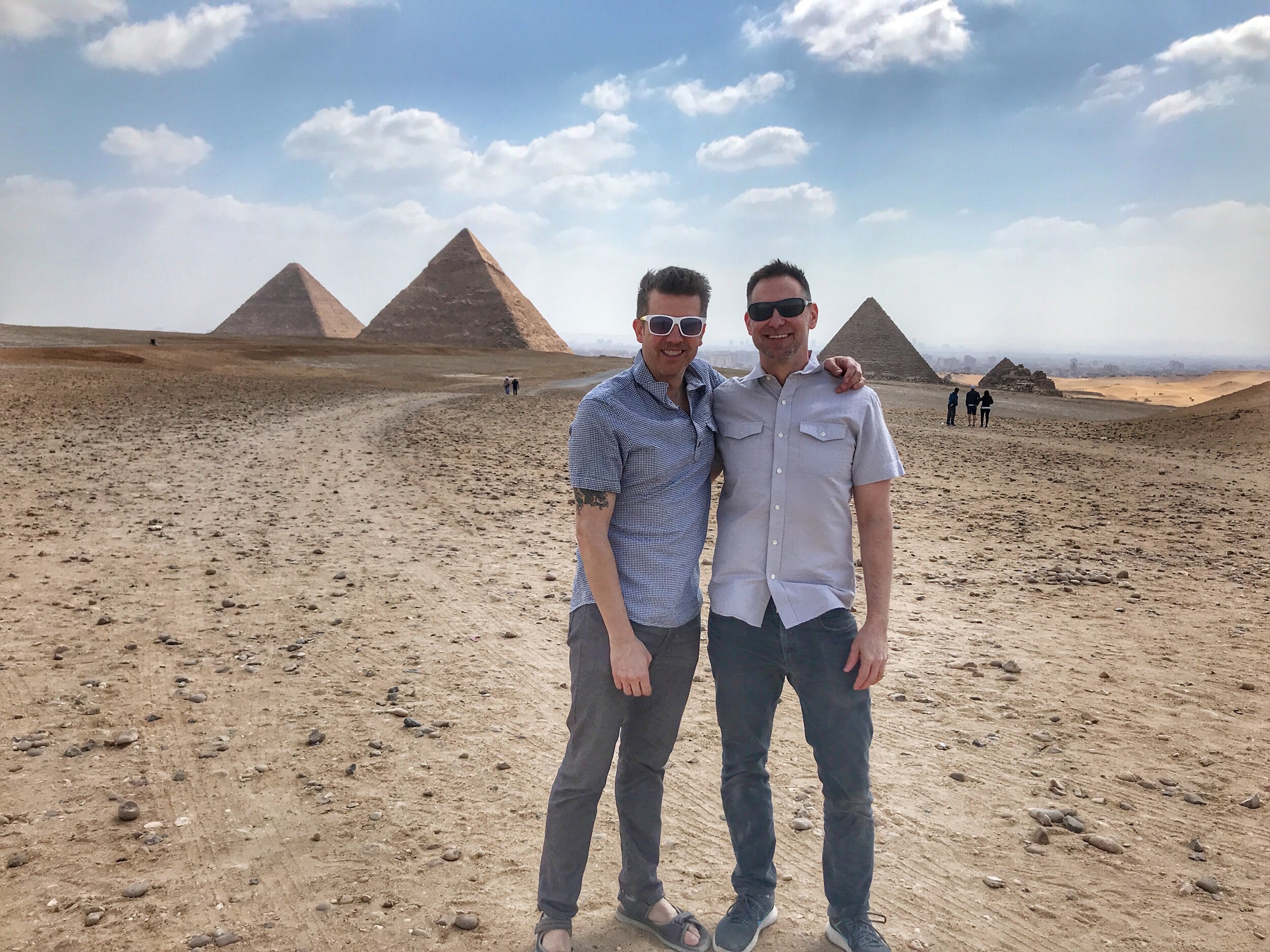
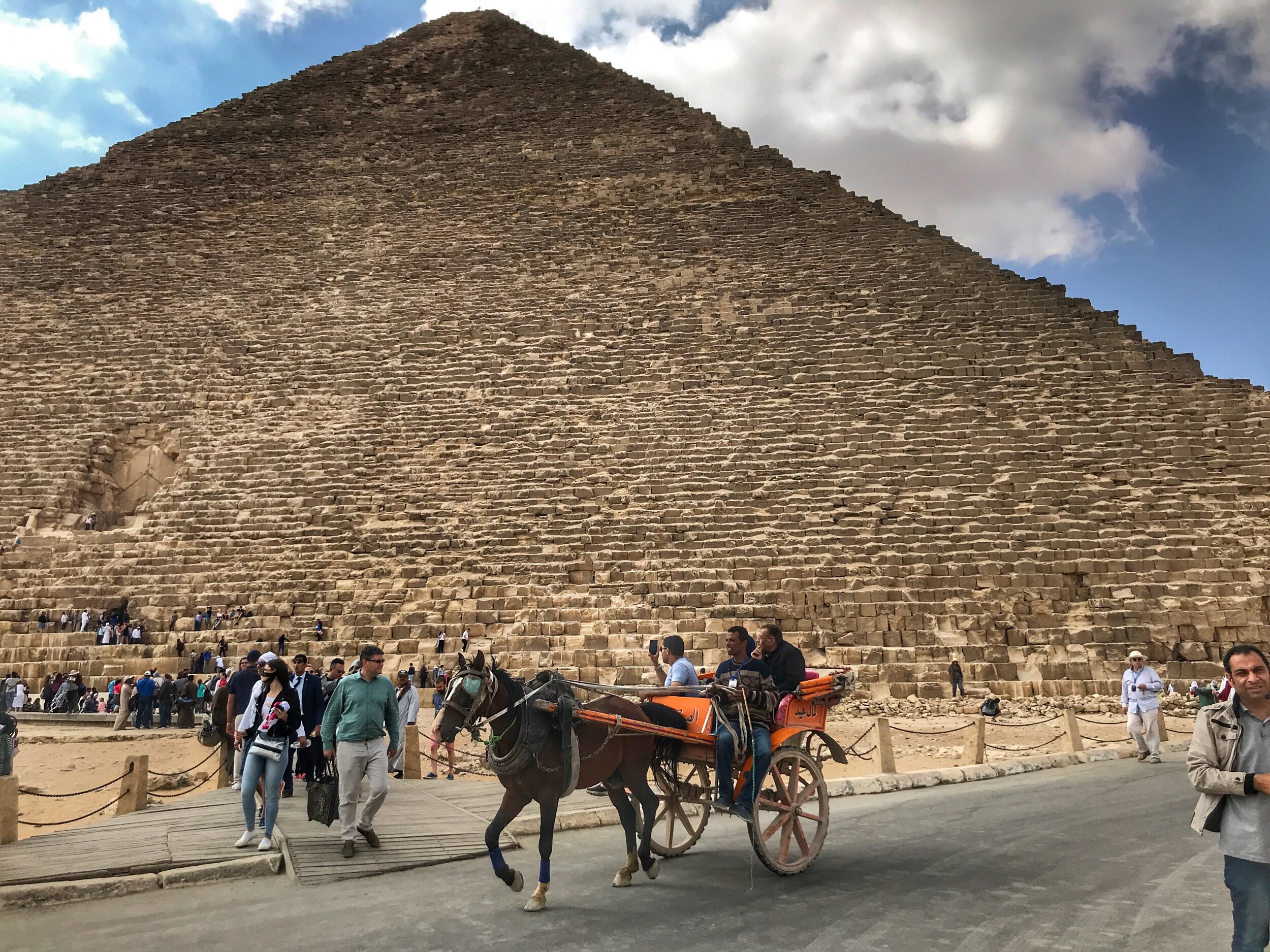
Don’t just see the Pyramids of Giza. The tombs at Saqqara are the architectural stepping stones that led to those wonders. Oh, and the Step Pyramid is the oldest building in the world.
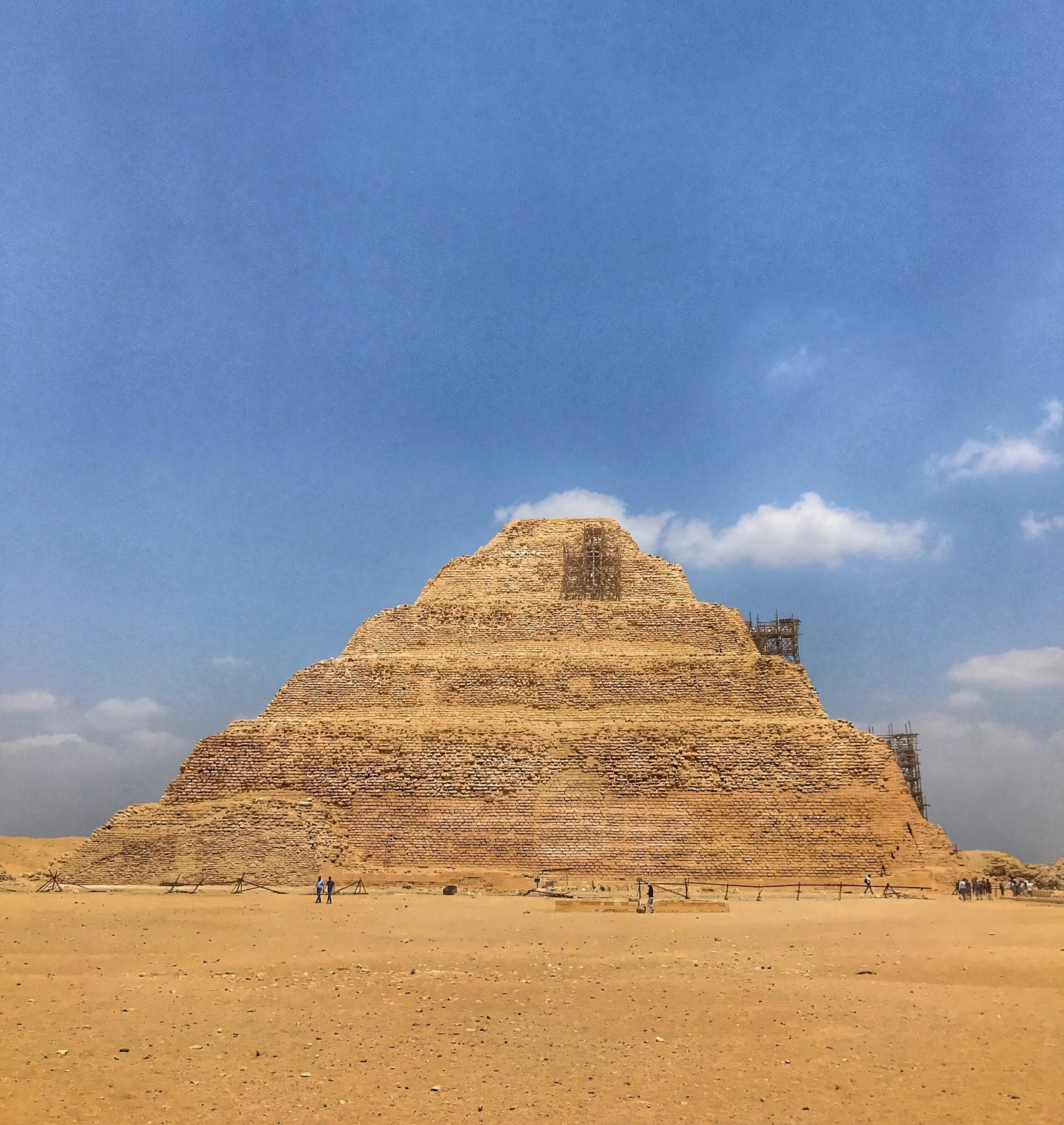
The tiered structure known as the Step Pyramid at Saqqara is the direct descendant of the smooth-surfaced Great Pyramids at Giza
Using a verbal sleight of hand to distract us after our whirlwind tour of the Giza necropolis, our guide Ahmed, who was selected for us by the Kempinski Nile Hotel in Cairo, began telling us about the history of Saqqara. He paused only briefly to encourage us to stop at a souvenir shop on the way, this one peddling papyrus or perfume, where he would surely get commission if we bought anything. Ahmed seemed to be a knowledgeable guide, but his lack of enthusiasm was glaringly obvious.
“Considered the first recorded architect in history, Imhotep designed the Step Pyramid at Saqqara and was later portrayed as an evil high priest who had been buried alive in ‘The Mummy.’”
After spending our morning getting rushed through the Pyramids and Sphinx, I mentioned stopping for lunch at the Marriott Mena House, having been told there was a spectacular view of the Pyramids while you ate alfresco. Ahmed replied that he had recently eaten there and dismissed it as overrated and ridiculously expensive, lying about the prices of the meals. It became clear that he wasn’t going to let us go there, even though it was part of our planned itinerary.
It was about this time that I turned to Wally and muttered, “We must have passed the Solar Boat Museum when we were leaving Giza.” We were both upset by this, never imagining we’d have a guide who wouldn’t even ask if we’d want to see the various sites at an attraction. There’s a good chance this would be our only time in Egypt and we wanted to see as much as we could — especially since we were paying for our guide and car service until 4 p.m.
But were in a stranger’s car in a foreign country and by this time too far away to go back.
Pharaoh Djoser commissioned the Step Pyramid for his tomb in 2630 BCE
Step on It
Frequently paired with the more famous Giza Plateau, the Saqqara necropolis is where the world’s oldest large-scale stone monument, the Step Pyramid of Djoser, was built. Admission costs 150 Egyptian pounds per person (a bit over $9 at the time of this writing).
Prior to its construction, Ancient Egyptian kings were buried beneath great oblong mud-brick structures with a flat roof and sloping sides known as mastabas. According to the Abydos King List, carved on a temple wall, Djoser was the first king of the Third Dynasty, and it was his 19-year reign that allowed the grandiose plan for his pyramid complex to be completed during his lifetime.
Built in stages, the Step Pyramid was constructed between 2630 and 2611 BCE. The tomb began as a traditional mastaba, but instead of mud-brick, it was built of stone taken from the nearby enclosed burial complex of Gisr el-Mudir. It was gradually enlarged, with smaller mastabas stacked on top of one another in concentric tiers to form the final height of 200 feet high — steps which the dead king could use to ascend into the heavens.
What’s truly amazing is that that’s just the beginning. What can’t be seen are the three miles of passageways and chambers that were carved beneath the pyramid!
Scaffolding covered parts of the Step Pyramid when we visited
When we visited the atmospheric Step Pyramid of Djoser, it was partially covered in scaffolding. Ahmed told us that it was closed due to ongoing conservation work and structural concerns after an earthquake in 1992.
Imhotep was many things, including the architect of the Step Pyramid at Saqqara — but a reanimated evil mummy he was not
Imhotep: The Man, the Myth, the Legend
A man named Imhotep was responsible for the design of the Step Pyramid of Saqqara. Considered the first recorded architect in history, he was later portrayed as an evil high priest who had been buried alive in The Mummy movie franchise. But he was actually just a mortal man whose name translated as “The One Who Comes in Peace.”
A savant who rose to the top of Egyptian society, Imhotep served as a scribe, architect and vizier in the court of Pharaoh Djoser. He was also a high priest of the creator god Ptah, physician and scientist. That talent would eventually lead to his posthumous deification as the patron god of medicine by the Egyptians and later by the Greeks as Asclepius.
Duke insisted we include a historically accurate image of Imhotep as well
King Djoser was so pleased with Imhotep’s work that he allowed the architect’s name to be inscribed on the pyramid along with his own.
Imhotep’s tomb is probably located at Saqqara but has yet to be found.
Fun fact: In 1964, archaeologist Walter Bryan Emery discovered a network of catacombs holding the remains of thousands of mummified ibises, long-legged, long-necked birds with downward-curving beaks, brought to the necropolis by pilgrims as offerings to the deified Imhotep. (These weren’t the only mummified animal remains found at Saqqara. Learn more about animal mummies here.)
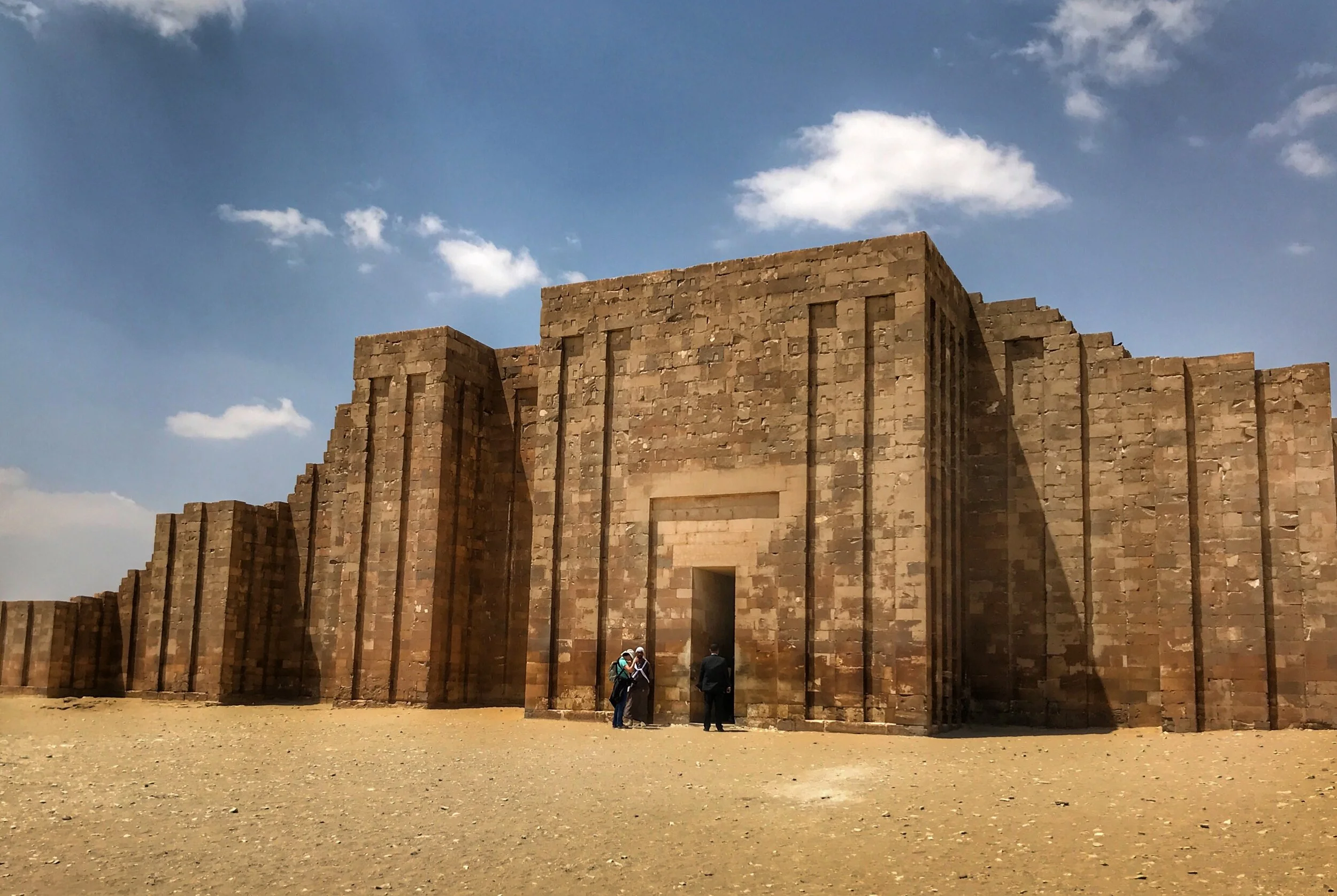
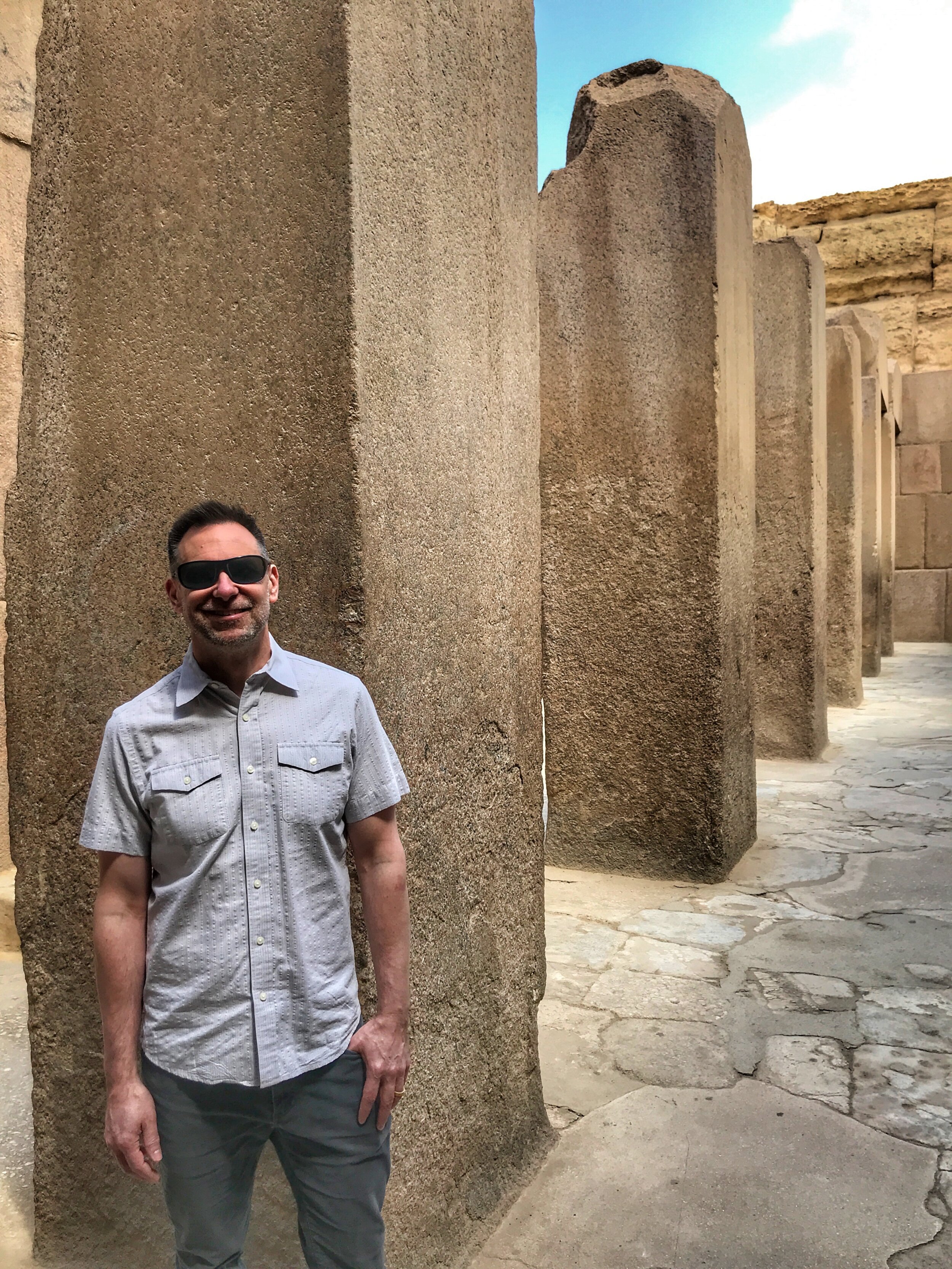
Some of the buildings of Ancient Egypt struck us as surprisingly modern, including the entrance hall to Djoser’s funerary complex
Entrance Hall Colonnade
Like Hatshepsut’s Mortuary Temple, the clean geometric exterior of Djoser’s entrance hall struck me as quite modern. There’s only one way into the complex, situated in the center of the largest bastion of the enclosure wall. The narrow hall is comprised of 20 pairs of columns, each connected to the side wall by masonry, as opposed to free-standing, and are carved to resemble bundles of reeds. The colonnade was probably once timber-roofed, though now austere concrete slabs hover high above these unique, but decaying, pillars.
The columns at Djoser’s complex aren’t in the best shape
Heb Sed Court
After passing through the entrance hall colonnade, Wally and I wandered over a low wall and into a sunken open-air courtyard with a raised stone platform. I later learned that this was known as the Heb Sed Court.
Beyond a pair of elevated shrines or chapels are replicas in stone of structures that would have been used for Heb Sed, the king’s jubilee festival marking the 30th year of a pharaoh’s reign. (As we know, Djoser never quite made it there.) One chapel appears to be a flat-roofed tentlike structure, while the other has a curved roof and false door, a symbolic passageway for the king’s ka, or spirit, to use in the afterlife.
While we enjoyed our visit, which also included an expedition into the Pyramid of Unas and the Mastaba of Mereruka, Ahmed never went beyond his own agenda and he certainly didn’t encourage us to explore. A lot of the information contained in our posts pertaining to Giza and Saqqara has been supplemented with our own research and curiosity about the sites. –Duke