Archeological evidence shows that the Israelites’ destruction of Jericho and the other cities of the Promised Land was nothing more than propaganda.
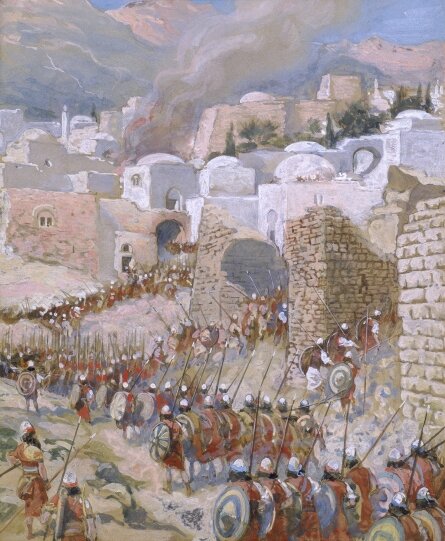
And the walls came tumbling down? Did the city of Jericho fall as it’s depicted in the Bible? The Taking of Jericho by James Tissot, circa 1902
I always felt bad for Moses. He suffered as his people were enslaved by the Egyptians and was instrumental in leading their escape — only to have them wander dejectedly through the desert for 40 years. And then, right as the Israelites were in sight of Canaan, at long last, poor old Moses keels over and dies. He never even got to set foot in the Promised Land.
It seems like a cruel trick: After leading his people out of slavery and then for 40 years in the desert, Moses gets a glimpse of the Promised Land — but dies before entering it.
Turns out the Israelites most likely didn’t go on to engage in a conquest of Canaan as the Bible says, according to Israel Finkelstein and Neil Asher Silberman in their book The Bible Unearthed: Archaeology’s New Vision of Ancient Israel and the Origin of Its Sacred Texts.
“Despite the string of fantastical victories described in the Bible, there’s no archeological evidence that the Israelites conquered the cities of Canaan. ”
At the time of the supposed conquest of cities like Canaan, the area was actually sparsely populated with no evidence of warfare.
Despite the string of fantastical victories described in the Old Testament of the Christians (the first five books of which make up the Jewish Torah), there’s simply no archeological evidence that the Israelites conquered the cities of Canaan.
In fact, at the time the conquest is said to have happened, in the Late Bronze Age, the cities of the region were sparsely populated.
And despite the description of the walls of Jericho miraculously tumbling down at the blowing of some trumpets, the towns of Canaan weren’t fortified. There would be ruins of stone walls from the time — but there simply aren’t any. Makes for a dramatic story, though.
A map of the Twelve Tribes of Israel from 1320
The First Israelites: A Peaceful, Gradual Expansion
Instead of a lengthy battle campaign in which the Israelites conquered the major cities of Canaan, archeological evidence points to a much more mellow birth of the Israelite people.
A dense network of about 250 highland villages in central Canaan developed in the span of a few generations around 1200 BCE. Most were no more than an acre in size, home to an average of 100 inhabitants, half of which were adults and half children.
There certainly wasn’t a strong cultural identity that united these people.
The Ancient Israelites didn’t go on a killing spree throughout Canaan; they arrived peaceably over the course of a few generations.
“In contrast to the culture of the Canaanite cities and villages in the lowlands, the highland villages contained no public buildings, palaces, storehouses or temples,” write Finkelstein and Silberman. “Signs of any sophisticated kind of recordkeeping, such as writing, seals and seal impressions, are almost completely absent. There are almost no luxury items: no imported pottery and almost no jewelry. Indeed, the village houses were all quite similar in size, suggesting that wealth was distributed quite evenly among the families.”
Also conspicuously absent for God’s supposed Chosen People: shrines or any other evidence of their religious beliefs.
The early Israelites seem to have eked out an agricultural existence. Stone-lined pits dug between houses stored grain, and fenced courtyards secured animal herds at night.
The Fall of Jericho by Tamás Galambos shows the city as a small metropolis. But the reality is that these were small unfortified villages.
Despite the biblical stories of conquest after conquest, the evidence shows that these people were actually peaceful. The villages weren’t fortified and showed no signs of burning or other sudden destructions that would indicate an attack. Nor were any weapons discovered during excavations.
The Ancient Israelites surely had a lot that differentiated them from other people in the area, like unique religious practices, right? Nope. Only one thing: an aversion to pork.
The One Defining Characteristic of the Early Israelites
As mentioned, the remains of these villages offer scant clues as to what set apart the Ancient Israelites. There simply isn't any evidence of religion or culture. But there is one item that’s conspicuously missing from their diet: pig bones. While these were found in neighboring lands, the lack of remains reveals that no pigs were raised in the highlands during the Iron Age, the era of the Israelite monarchies.
So what made the early Israelites unique? They didn’t eat pork. Th-th-th-that’s all, folks.
“Half a millennium before the composition of the biblical text, with its detailed laws and dietary regulations, the Israelites chose — for reasons that are not entirely clear — not to eat pork,” Finkelstein and Silberman write. “When modern Jews do the same, they are continuing the oldest archaeologically attested cultural practice of the people of Israel.”
This site, known as the Tower of Jericho, reveals that the conquest of Canaan didn’t happen like the Bible says.
Contrary to the Bible
The archeological evidence just doesn’t support the tales of the Old Testament, the authors argue. In fact, it’s the exact opposite: “the emergence of early Israel was an outcome of the collapse of the Canaanite culture, not its cause,” they write. “And most of the Israelites did not come from outside Canaan — they emerged from within it. There was no mass Exodus from Egypt. There was no violent conquest of Canaan. Most of the people who formed early Israel were local people — the same people whom we see in the highlands throughout the Bronze and Iron Ages. The early Israelites were — irony of ironies — themselves originally Canaanites!” –Wally